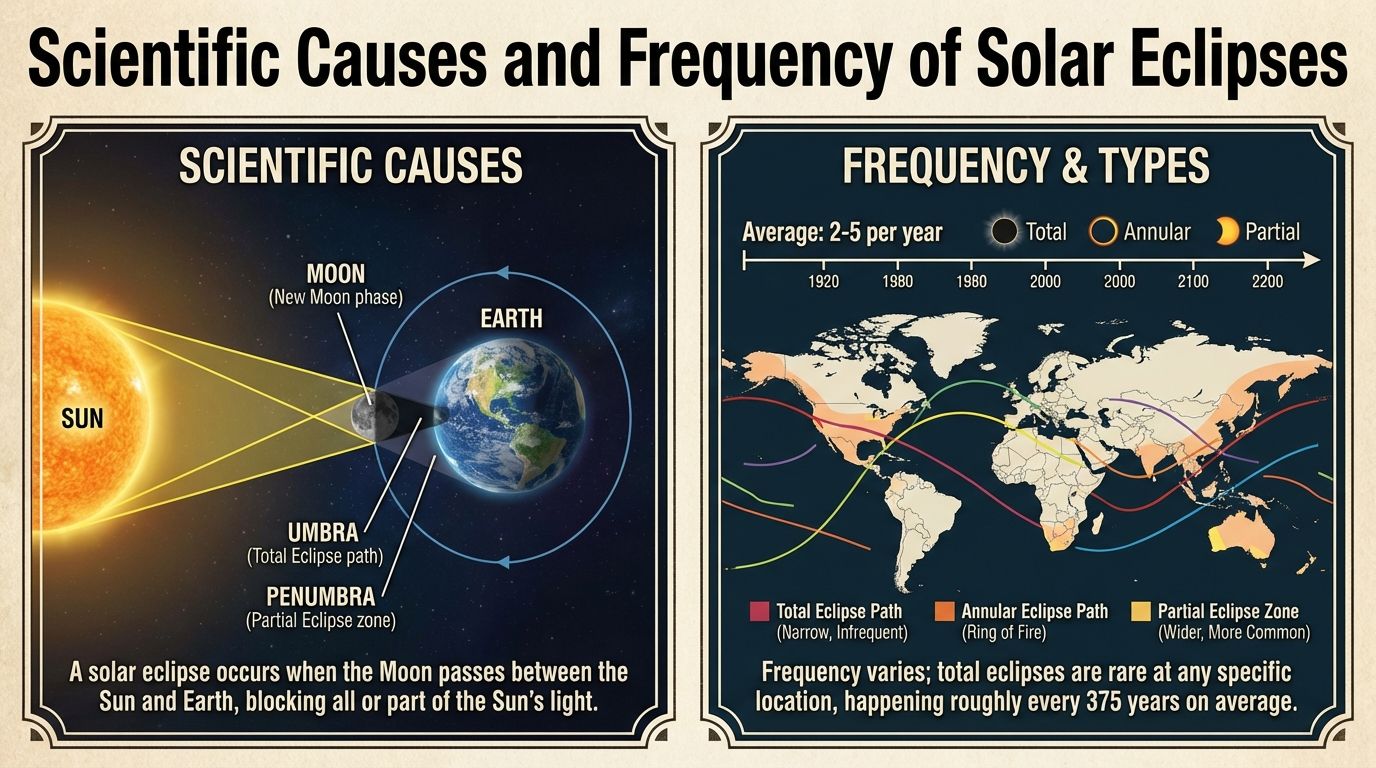
The Sun is the heart of our solar system, a radiant sphere that makes life possible on Earth. It shapes our days, seasons, and even our moods. Yet despite how familiar it feels, the Sun is full of fascinating secrets. From its fiery layers to the quiet influence it has on weather and tradition, here’s everything you didn’t know you needed to know about our closest star.
The Sun is more than just a light source. It’s a living engine of energy, rhythm, and balance. It drives our weather, marks time, and connects science with spirit.
1. The Sun Is a Star, Not a Planet
Although it dominates our sky, the Sun is just an ordinary star among billions in the Milky Way. It’s classified as a G-type main-sequence star, or a “yellow dwarf.” You can learn more about its daily patterns and behavior at sun data.
2. It’s About 4.6 Billion Years Old
Scientists estimate the Sun formed from a massive cloud of dust and gas roughly 4.6 billion years ago. It’s in its middle age, shining steadily before it will eventually become a red giant.
3. The Sun Makes Up 99.8% of the Solar System’s Mass
Almost all the mass of our entire solar system is packed inside the Sun. That’s why its gravity keeps all the planets, asteroids, and comets locked in orbit.
4. The Sun’s Surface Isn’t Solid
What looks like a surface is actually a layer of hot plasma called the photosphere. Temperatures there reach about 10,000 °F. The Sun doesn’t have a crust like Earth; it’s a churning sphere of gas and light.
5. Sunlight Takes About 8 Minutes to Reach Earth
Light travels at nearly 186,000 miles per second, but the Sun is about 93 million miles away. When you see the Sun, you’re actually looking eight minutes into the past.
Those eight minutes of travel time mean that even a small solar flare reaches us nearly instantly. Stay updated on real-time solar activity and daylight timing at daylight chart.
6. The Sun Has Layers Like an Onion
It’s made up of several parts: the core, the radiative zone, the convective zone, the photosphere, the chromosphere, and the corona. Each plays a role in producing the heat and light we depend on.
7. Sunspots Are Cooler, Magnetic Regions
Sunspots appear darker because they’re slightly cooler than surrounding areas. They’re signs of magnetic turbulence, part of the Sun’s 11-year activity cycle.
8. The Sun Powers Earth’s Weather
Every breeze, storm, and rainfall begins with solar energy. Uneven heating of the atmosphere creates winds and pressure systems. For daily updates on how sunlight influences local weather, check weather forecast.
9. The Sun Shapes the Rhythm of Day and Night
As Earth spins, we experience sunrise and sunset, creating the daily cycle that defines our routines. To understand how daylight varies with season and latitude, read sunrise seasons.
10. Sunrise Marks the Sun’s Daily Return
Every morning, sunlight creeps over the horizon, painting the sky in warm colors. That moment signals the Sun’s apparent rebirth each day. To explore the beauty and timing of dawn, visit twilight guide.
11. The Sun Has Deep Cultural Meaning
For millennia, people have worshiped, prayed to, and celebrated the Sun. It symbolizes life, rebirth, and divine power. Ancient Egyptians honored Ra the Sun god, while in Japan Amaterasu represents light and purity. Learn more about cultural rituals tied to sunlight in sun rituals.
| Culture | Sun Symbolism |
|---|---|
| Egyptian | Ra – the Sun God |
| Japanese | Amaterasu – goddess of the Sun |
| Incan | Inti – source of life |
| Hindu | Surya – charioteer of dawn |
12. Animals Respond to the Sun’s Cycle
Many animals rely on sunlight to time their activity. Roosters, for example, crow just before sunrise because their internal clocks sense changes in light. To learn how and why they do this, read rooster behavior.
13. The Sun Fuels Exploration and Inspiration
From sailors who steered by its light to hikers who chase dawn from mountain peaks, the Sun has always guided adventure. For travelers seeking the best sunrise experiences, check sunrise hikes.
14. Sunlight Affects Human Health
Sun exposure helps the body produce vitamin D, crucial for bone and immune health. It also boosts serotonin levels, improving mood and focus. Just a few minutes outdoors each morning can balance body rhythms naturally.
- Morning light helps regulate sleep cycles.
- It enhances concentration and memory.
- It supports immune function and mood stability.
- It promotes healthy skin and vitamin D production.
15. The Sun Will Eventually Transform
In about 5 billion years, the Sun will expand into a red giant and engulf Mercury and Venus. Eventually, it will shrink into a white dwarf, a quiet ember of what once was. But for now, it continues to shine; steady and strong.
The Sun’s journey may be long, but its daily rising is a reminder of renewal. Embrace that energy - Use the first light as a cue to reset your day with calm intention.
The Heart of Every New Day
The Sun has watched Earth grow, evolve, and change. It shapes our lives, dictates time, and fuels hope. Whether viewed from a busy city rooftop or a quiet trail, its steady glow connects every living thing beneath it. The next time sunlight touches your face, pause for a moment, you’re feeling the heartbeat of our solar system.